import random
numbers = []
for i in range(10):
numbers.append(random.randint(0,100))
print("Random List")
print(numbers)
Explore
Get into groups of 3
We will be focusing on 4 algorithms today.
We will look at the first one together, Bubble Sort
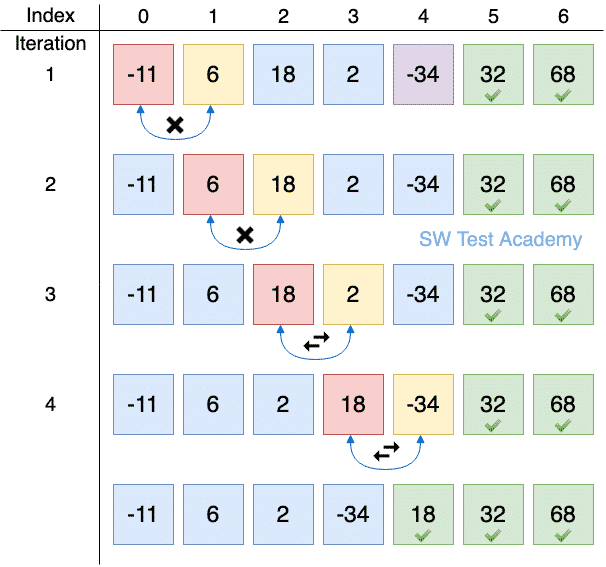
What is happening with this sort?
Check two values, if it's smaller they swap, if not, they keep going.
In your groups you will each choose to be an expert on a sorting algorithm. Merge, Selection, and Insertion. Take about 5 minutes to read about your algorithm and be ready to explain it to your other group members.
Practice
[75, 17, 46, 80, 67, 45, 69, 79, 40, 0]
How would you sort this list with...
- Bubble Sort- compare the first number to the second and if it's greater, move it forward, if not, keep it in the same space, continue until it's all sorted. Ex: compare 75 and 17, 75 is greater so switch the two numbers. 75 is greater than 46 so switch the two numbers and continue until all sorted.
- Selection Sort- moves all the sorted to the right, and only goes through the unsorted. put 0 in the beginning and put the rest of the list to the right, and find the next smallest number and put it next to 0 which would be 17, then continue.
Explain.
[88, 39, 53, 39, 58, 43, 74, 81, 71, 51]
How would you sort this list with...
- Merge Sort- splits the list in half and then keeps splitting until you can't split anymore. Then, merge the lists in order, then merge and order the lists. Split into 88, 39, 53, 39, 58 and 43, 74, 81, 71, 51. Keep splitting and then start merging them into order. Once the two lists are sorted merge them together from lowest to gretaest.
- Insertion Sort- ideal if part of the list is sorted already, when you get to one that needs to be swapped, you use the one that has been swapped and compare it to the rest of the list. swap 88 and 39, then swap 53 and 88, then compare 39 to all the ones before.
Explain.
Sorting Words
Sorting strings works in the same way as integers. Using your expertise algorithm, sort the following list of random words.
I would use bubble sort and take the first letter of each word, if the letter comes later in the alphabet then swap. Continue with the bubble sort until it is sorted alphabetically.
import nltk
import random
nltk.download('words') # Download the word list (only required once)
from nltk.corpus import words
english_words = words.words()
#print(len(english_words)) # Prints the number of words in the list
# You can now use the 'english_words' list in your code
words = []
for i in range(10):
words.append(english_words[random.randint(0,len(english_words))])
sorted_words = sorted(words)
print("Random List")
print(words)
print("Sorted Words:")
print(sorted_words)
Discuss
Answer the following with your group.
- When should you use each algorithm? What makes an algorithm the right choice?
- Given the following lists...
- [0, 2, 6, 4, 8, 10]: insertion because part of the list is already sorted so you would just use one element and compare it to all the numbers and swap accordingly.
- [Elephant, Banana, Cat, Dog, Apple]: selection, takes the first letter in alphabet and puts it in the front, then continues until alphabetically sorted.
- [29, 13, 83, 47, 32, 78, 100, 60, 65, 15, 24, 9, 40, 68, 53, 8, 90, 58, 39, 32, 34, 91, 74, 94, 49, 87, 34, 87, 23, 17, 27, 2, 38, 58, 84, 15, 9, 46, 74, 40, 44, 8, 55, 28, 81, 92, 81, 88, 53, 38, 19, 21, 9, 54, 21, 67, 3, 41, 3, 74, 13, 71, 70, 45, 5, 36, 80, 64, 97, 86, 73, 74, 94, 79, 49, 32, 20, 68, 64, 69, 1, 77, 31, 56, 100, 80, 48, 75, 85, 93, 67, 57, 26, 56, 43, 53, 59, 28, 67, 50]: merge, since this is such a big list, merge would split the list in half and continue splitting in half, then merge back into order for each list until the lists come back to one big list. This would happen in a kind of parallel processing so that the lists merge and split at the same time. Select the algorithm you believe is best for each, explain.
HACKS
Provided below is a Bubble Sort Algorithm sorting a list of dictionaries based off of selected key.
Now it's time to do some coding...
Run code and then research and answer these questions...
Is a list and/or dictionary in python considered a primitive or collection type? Why?
A list and dictionary are both considered collection types in python. Primitive types are integers, strings, booleans, and cannot hold and organize multiple values or objects.
Is the list passed into bubble sort "pass-by-value" or "pass-by-reference? Describe why in relation to output.
the list passed into bubble sort is passed by reference. This means that the actual list object is being modified within the function, and any changes made to the list will be reflected outside the function as well. The function operates on the actual object passed in rather than a copy of it.
- Implement new cell(s) and/or organize cells to do the following.
- Create your own list
- Use your expertise sorting algorithm (selection, insertion, merge). Note, I got my bubble sort from Geek for Geeks and made modifications. Each student in a group should have a unique algorithm.
- Test your list with my bubble sort
- Test my list with your new sort, do NOT make a copy of my list when doing this
- Research analysis on sorting:comparisons, swaps, time. Build this into your hacks. - Find a better way to print the data, key first, then other elements in viewable form.
Use the code below to help guide your adventure
"""
* Creator: Nighthawk Coding Society
Bubble Sort of a List with optimizations
"""
# bubble sorts a list of dictionaries, base off of provided key
def bubbleSort(list, key):
n = len(list) - 1 # list are indexed 0 to n-1, len is n
# Traverse through list with i index
for i in range(n):
swapped = False # optimize code, so it exits if now swaps on inner loop
# Inner traversal using j index
for j in range(n-i): # n-i as positions on right are in order in bubble
# Swap if the element KeyN is greater KeyN1
keyN = list[j].get(key)
keyN1 = list[j+1].get(key)
if keyN > keyN1:
swapped = True
list[j], list[j + 1] = list[j + 1], list[j] # single line swap
if not swapped: # if no swaps on inner pass, list is sorted
return # exit function
if __name__ == "__main__":
# list/dictionary sample
list_of_artists = [
{"artist": "Lizzy McAlpine", "age": 23, "album": "Five Seconds Flat"},
{"artist": "Lorde", "age": 26, "album": "Solar Power"},
{"artist": "grandson", "age": 29, "album": "I Love You, I'm Trying"},
{"artist": "Bazzi", "age": 25, "album": "Infinite Dream"}
]
# assuming uniform keys, pick 1st row as source of keys
key_row = list_of_artists[0]
# print list as defined
print("original")
print(list_of_artists)
for key in key_row: # finds each key in the row
print(key)
bubbleSort(list_of_artists, key) # sort list of artists
print(list_of_artists)
def mergeSort(arr, key): # arr: array represents list of peoplelist_of_people we want to sort
if len(arr) <= 1: # if only 0 or 1 element, list already sorted
return arr
# divide into two halfs: left and right
mid = len(arr) // 2
left = arr[:mid]
right = arr[mid:]
# sort left and right halves
left = mergeSort(left, key)
right = mergeSort(right, key)
# merge sorted halves
return merge(left, right, key)
def merge(left, right, key):
result = []
i = 0 # index for left sublist
j = 0 # index for right sub list
# Compare and merge elements from the left and right sub-lists
while i < len(left) and j < len(right):
if left[i].get(key) <= right[j].get(key):
result.append(left[i]) # Add the element from the left sub-list to the result
i += 1
else:
result.append(right[j]) # Add the element from the right sub-list to the result
j += 1
# Add any remaining elements from the left sub-list
while i < len(left):
result.append(left[i])
i += 1
# Add any remaining elements from the right sub-list
while j < len(right):
result.append(right[j])
j += 1
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
# list/dictionary sample
list_of_people = [
{"name": "Risa", "age": 18, "city": "New York"},
{"name": "John", "age": 63, "city": "Eugene"},
{"name": "Shekar", "age": 18, "city": "San Francisco"},
{"name": "Ryan", "age": 21, "city": "Los Angeles"}
]
# assuming uniform keys, pick the first row as the source of keys
key_row = list_of_people[0]
# print the list as defined
print("original")
print(list_of_people)
for key in key_row: # find each key in the row
print(key)
sorted_list = mergeSort(list_of_people, key) # sort the list of peoplelist_of_people
print(sorted_list)
Analysis on Sorting
Comparisons:
number of times the algorithm compares two elements in the list to determine their order. In merge sort, comparisons occur when merging the sub-lists. On each comparison, the algorithm decides which element should come first in the sorted order.
Swaps:> number of times the algorithm exchanges the positions of two elements in the list. In merge sort, swaps do not occur because the algorithm creates a new sorted list by merging the sub-lists. It avoids swapping elements within the original list. Time:
estimate of how the algorithm's performance scales with the input size. Merge sort has a time complexity of O(n log n), where n is the number of elements in the list. This means that as the list size doubles, the time taken to sort it will increase by a factor of approximately two times the logarithm of the list size.
More Readable Format
def mergeSort(arr, key):
comparisons = 0 # Track the number of comparisons
swaps = 0 # Track the number of swaps
# If the array has 0 or 1 element, it is already sorted
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr, comparisons, swaps
# split into sublists
mid = len(arr) // 2
left = arr[:mid]
right = arr[mid:]
# Recursively call mergeSort on left and right halves
left, left_comparisons, left_swaps = mergeSort(left, key)
right, right_comparisons, right_swaps = mergeSort(right, key)
# Update the total comparisons and swaps
comparisons += left_comparisons + right_comparisons
swaps += left_swaps + right_swaps
# Merge the sorted left and right halves
merged, merge_comparisons, merge_swaps = merge(left, right, key)
# Update the total comparisons and swaps
comparisons += merge_comparisons
swaps += merge_swaps
return merged, comparisons, swaps
# Rest of the code remains the same...
if __name__ == "__main__":
list_of_artists = [
{"artist": "Lizzy McAlpine", "age": 23, "album": "Five Seconds Flat"},
{"artist": "Lorde", "age": 26, "album": "Solar Power"},
{"artist": "grandson", "age": 29, "album": "I Love You, I'm Trying"},
{"artist": "Bazzi", "age": 25, "album": "Infinite Dream"}
]
key_row = list_of_artists[0]
print("Original List:")
for artist in list_of_artists:
for key, value in artist.items():
if key != "artist":
print(f"{key}: {value}")
print("------")
# Sorting and printing with merge sort
for key in key_row:
sorted_list, comparisons, swaps = mergeSort(list_of_artists, key)
print(f"\nSorted List by '{key}':")
for artist in sorted_list:
for key, value in artist.items():
if key != "artist":
print(f"{key}: {value}")
print("------")
print("Comparisons:", comparisons)
print("Swaps:", swaps)